STRUCTURE OF HUMAN EYE AND ITS WORKING
The human eye has been called the most complex organ in our body. It is amazing that so small can have so many parts. Eye is a natural optical instrument. It is present in the form of eyeball in the sockets of our skull. Its diameter is approximately 2.5 cm.
Three layers of eye ball:
- Outermost layer – Sclera
- Middle layer – choroid
- Innermost layer – retina
- Sclera:
It is the outermost, white, tough layer. It covers the whole part of the eyeball. It protects the eyeball. The front portion of the sclera is known as cornea.
- Cornea:
Cornea is covered by a thin, transparent membrane known as conjunctiva. Conjunctiva helps the eye to be moist and prevent the dryness.
- Choroid:
It is the middle layer of the eyeball. It is made up of connective tissue. It is red brown in color. It provides the nutrition to the eye.
- Iris:
It is circular, colored area of the eye that surrounds the pupil. It is found in different colors like brown, black, blue, green, etc.
- Function of Iris:
It controls the amount of light that enters the eye.
- Pupil:
It is an aperture which enlarges and shrinks like a diaphragm of a camera lens.
- Function of Pupil:
It allows the light to enter through the eye lens.
- IMPORTANT POINTS :
- The iris allows more light into the eye when environment is dark and allows less light into the eye when environment is bright.
- The size of pupil is control by the action of papillary sphincter muscle and dilator muscle.
- Eye lens:
Behind the iris, there is a transparent biconvex structure holed by cilliary muscles are known as eye lens.
- Function of eye lens:
It helps to focus the light on the retina.
- Cilliary muscles:
It holds the eye lens and adjusts the focal length of the eye lens so that any object can be seen clearly.
- Retina:
It is the innermost layer of the eyeball. Retina contains blood vessels that nourish them. Retina also has two types of photoreceptors: rods and cones.
The most sensitive part of retina is a small area known as Macula where millions cones are tightly packed.
- Important Points:
- High density of cones in macula makes the visual images detailed.
types of photoreceptoRs
There are two types of photoreceptors:
- Cones:
Cones are responsible for sharp, detailed central and color vision. They are mainly clustered in macula. These cells are less sensitive to light.
- Rods:
Rods are responsible for night and side vision. These cells are more sensitive to light. These are mainly clustered in peripheral areas of the retina.
- Important points:
- Rods are more numerous than cones.
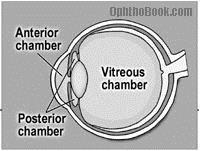
Chambers of eye ball
The eyeball is divided into two chambers:
- Anterior chamber:
It is the space between the inner part of the cornea and the eye lens. It has a fluid known as aqueous humor. Aqueous humor contains mainly water and a little amount of salt.
- Posterior chamber:
It is the space between the lens and retina. It has a jelly like fluid known as vitreous humor. Vitreous humor contains water, salt and albumin protein. It nourishes the retina.
- Important points:
- Both these fluids generate pressure to fill out the eye ball.
- It also helps to maintain its shape.
Working of eye
When light enter into the eye it passes through pupil. Iris controls the amount of the light. The cilliary muscles help the lens to focus the object on the retina. When light strikes on either on the rods or the cones of the retina, it is converted into an electric signal. The photoreceptors in the retina convert the light into the electrical signals. These signals carried to the brain by optic nerves and nerve fibers. The brain then translates the electrical signal into images we see.
Each eye has own optic nerve and nerve fibers. Both optic nerves meet at the optic chiasm. From the optic chiasm, half of the optic nerve from each side cross to the other side and run (continue) to the backside of the brain.
Thus the right side of the brain receives impulses from the left optic nerve as well as right optic nerve and the left side of the brain receives impulse from the right optic nerve as well as the left optic nerve. Then the brain integrates the information to produce a complete picture.
Defects of the eye
A clear image is formed only when the light rays from the object is focused on the retina. But whenever it does not happen; eye cannot form a clear image. The formed images are blurred. This is known as the defects of the eye. Now we are going to discuss about them.
- Nearsightedness:
In this type of the defect of the vision, far objects appear blurred but near objects are seen clear. This type of defect of vision also known as myopia.
- Position of images:
- In such a defective eye, image of the distant object is formed in the front of retina.
- This defect arises because of :
- The power of the eye increases.
- The focal length of the lens decreases.
- This may arise due to either:
- Elongation of the eyeball
- Excessive curvature of the cornea.
- Correction:
- This defect can be corrected by wearing glasses with concave lenses.
- Farsightedness:
This is also known as hyperopia. In this type of the defect of vision, near objects appear blurred but far objects are seen clear.
- Position of the images:
- In such a defective eye, the image of the near objects is formed behind of the retina.
- The cause of Arisen:
- The power of the eye decrease.
- The focal length of the lens increases.
- This defect may arise due to either:
- The eyeball becomes too shorter.
- Correction:
- This defect can be corrected by wearing glasses with convex lens.
- Astigmatism:
This defect is when the light rays do not all come to a single focal point on the retina, instead some focus on the retina and some focus in the front of the retina and some focus on the behind of the retina. Due to this, the person cannot simultaneously focus on both horizontal and vertical lines. This results in objects in one direction being well focused, while others in the perpendicular direction not well focused.
- Causes:
- This is usually caused by a non uniform curvature of the cornea.
- Correction:
- This defect can be corrected by using eye glasses with special spherical cylindrical lenses.
- Colour blindness:
In such a defective eye, images are clear but colors are not.
- Reasons:
- Absence of cones photoreceptors in retina.
- It may or may not be hereditary and cannot be corrected completely.
- Glaucoma:
We well known that there are two chambers in the eye ball. Both are filled with fluid. This fluid is produced in the posterior chamber and drain out from the anterior chamber through a complex drainage system. In this way, a balance is maintained between production and drainage of the fluid. This determines the Intra Ocular Pressure (IOP).
Due to malfunctioning of drainage of fluid, Intra Ocular Pressure (IOP) increases in the posterior chamber which damages the optic nerve. If it cannot be treated in time, it causes permanent loss of vision.








Topics are not categorise .
LikeLike
Its great and has helped me a lot
LikeLike
THANKS ROHIT…:)
LikeLike
Hello,
I have a couple of questions about the structure and control of the lens.
1) The connections from an outside ring connects the “hairs” to the lens, Sorry I do not know the correct name for the hairs.Is this ring fixed or floating in the eye?
2) If I could put a soft lens in with a very low Durometer I could I connect a nano circuit to it with a lot of “springs”? Think of it as as round trampoline with adjustable tension. .
3) I need to know what signals come to the lens to control its focus. Chemical, electrical, I do not care. I can convert them, and the brain will adapt over time, or I can accommodate it by changing the circuit.
I would appreciate your consideration on this. It may just be a brain exercise for me.
Regards,
John Nicosia
Honey Bear Electronics
(727) 741-2208
LikeLike
Help me a lot in exam times
LikeLike
best of luck for your results
thanks for watching my videos
LikeLike
nice… explanation..thankyou so much
LikeLike
my pleasure
LikeLike